
The most common scenario for this is adding new static MAC+IP mappings for the network's DHCP server. Sometimes, one needs to edit the network definition and apply the changes on the fly.
#How to have 2 active network connections on mac mac#
the MAC address is optional and will be automatically generated if omitted. Add the following snippet of XML to the config file:
to connect a guest to the 'default' virtual network, you need to edit the domain configuration file for this guest: Once the host configuration is complete, a guest can be connected to the virtual network based on the network name. If you are already running dnsmasq on your machine, please see libvirtd and dnsmasq. Some other applications may disable it, so the best option is to add the following to /etc/nf It will also attempt to enable ip_forward. Libvirt will add iptables rules to allow traffic to/from guests attached to the virbr0 device in the INPUT, FORWARD, OUTPUT and POSTROUTING chains. Do not add interfacesīridge name bridge id STP enabled interfaces
/how-to-connect-ethernet-to-a-mac-52108981-0a48976da953450285fc0805837292f4.jpg)
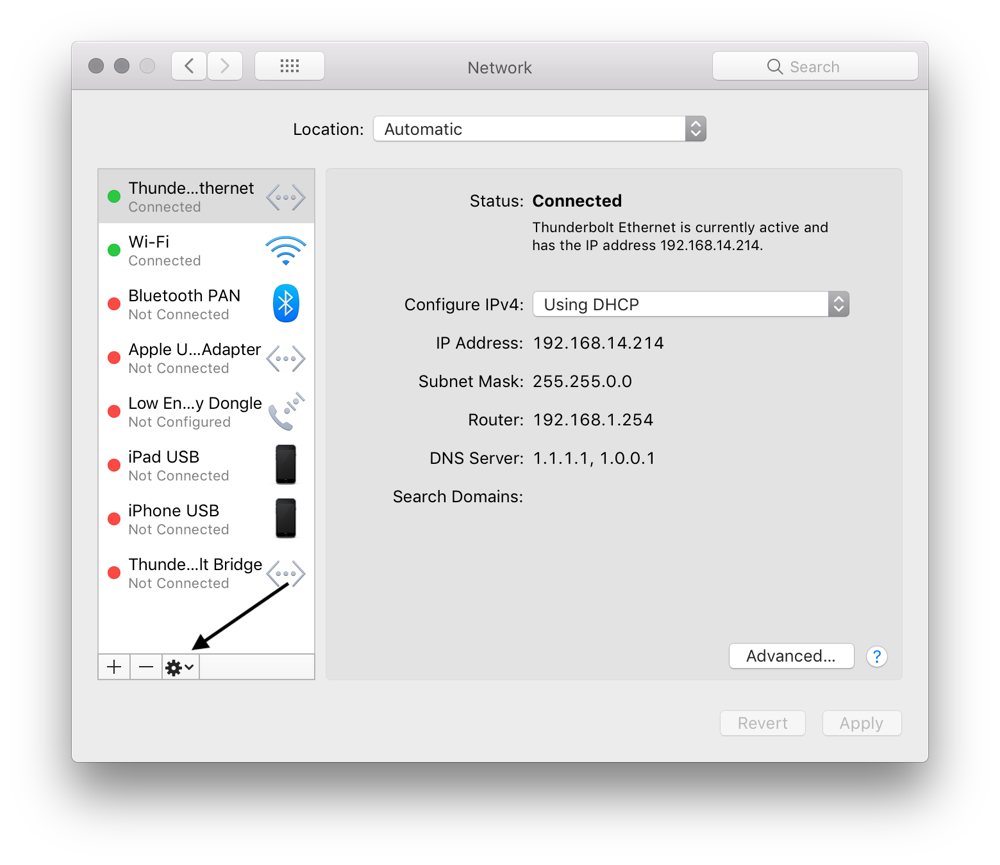
This device explicitly does *NOT* have any physical interfaces added, since it uses NAT + forwarding to connect to outside world. When the libvirt default network is running, you will see an isolated bridge device. Network default defined from /usr/share/libvirt/networks/default.xml # virsh net-define /usr/share/libvirt/networks/default.xml If it is missing, then the example XML config can be reloaded & activated This is the so called 'default virtual network'. NAT forwarding (aka "virtual networks") Host configurationĮvery standard libvirt installation provides NAT based connectivity to virtual machines out of the box. 3.3 Assignment from a pool of SRIOV VFs in a libvirt definition.3.2 Assignment with (SRIOV devices only).3 PCI Passthrough of host network devices.2.1.1.2 Disabling NetworkManager (for older distros).2 Bridged networking (aka "shared physical device").1.3 Applying modifications to the network.1 NAT forwarding (aka "virtual networks").Click the More Options link, which is a round icon with three dots inside, and then select Set Service Order.You will see the list of network services like Wi-Fi, Thunderbolt etc.Select the Location you want to edit by opening the Location drop-down menu.For example, your Mac will first try to connect to the Internet using the one at the top and if that is unsuccessful, it will go down the list until it connects successfully. You can change the network service order. The name Automatic indicates that your Mac will search all active network ports for the Internet. Ports, also called network services, are used to connect to the Internet – like Wi-Fi or Ethernet. By default, the Automatic location has made all available ports active. When you open the Network settings, you will see a location called “Automatic.” This was created by macOS as the default setting. Your “Automatic” location will not be affected by these changes. All changes will be saved to this location. Now you can make changes to this location.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
